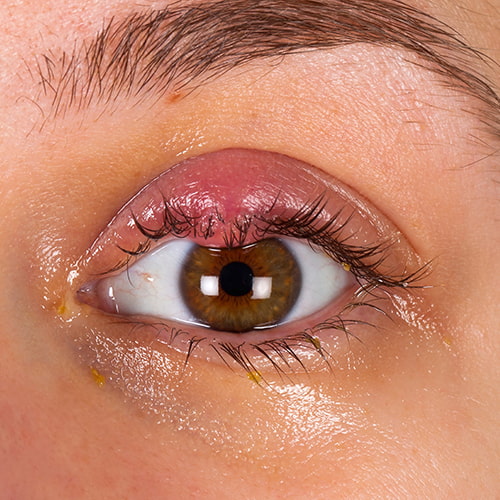
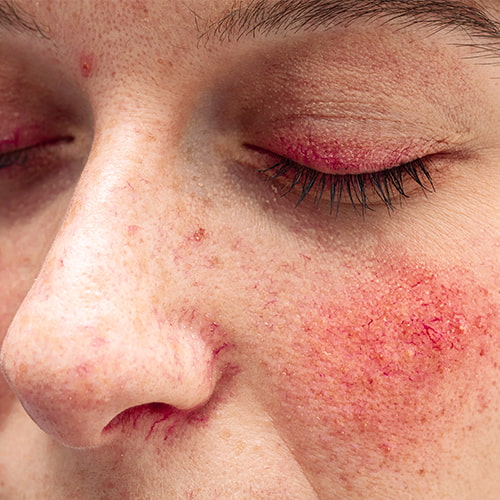
What is Demodex Hair Loss?
Hair loss is a frustrating issue that can affect anyone in any age group, and it can be more troublesome if it happens in the prime of your life. So, we decided to discuss this widespread issue in this post. We will tell you some hair care tips for avoiding hair loss after a brief explanation of its types, symptoms and causes.
Furthermore, we will discuss Demodex hair loss, which is related to a kind of skin parasite called Demodex mites.

What is Hair Loss?
Hair loss, also known as “alopecia” or “baldness,” refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically, the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. In most cases, inflammation or scarring is not present, and the strands can grow again after determining the cause. However, hair loss in some people can cause psychological distress and lack of confidence.
Types of Hair Loss

Symptoms of Hair Loss
1. Gradual thinning on top of the head
Hair thinning is a common sign of hair loss, which usually develops gradually without attracting much attention. In men, the hairline usually recedes, while in women, it does not, and only the hair on top of the head becomes thinner.
2. Circular or patchy bald spots
If your hair falls out in small, round patches, this is a sign that you may have a type of alopecia called alopecia areata. Patches of hair loss usually affect the scalp. However, they may also involve other parts of the body, such as the beard or eyebrows.
3. Sudden loosening of hair
Handfuls of hair may come out when you comb or wash your hair. You also notice more fallen hair strands compared to the usual shed on your pillows and sheets. This symptom is the most prominent sign of hair loss in both women and men. Sometimes the hair roots become so weak that strands separate even after gentle tugging. This symptom usually happens after a physical or emotional shock. This type of hair loss usually causes overall hair thinning and not bald patches.
4. Full-body hair loss
If you notice the loss of hair all over your body, this is probably a temporary condition. This type of hair loss usually occurs after specific treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The hair usually comes back after you have stopped the procedure.
5. Patches of scaling that spread over the scalp
Patches of scaling that spread over the scalp are signs of hair loss caused by ringworm. Contrary to its name, this type of alopecia is not associated with any worm, but rather infection with a fungus may be accompanied by broken hair, redness, swelling and, at times, oozing.
Take Online Demodex Quiz
Test Demodex mite populations online with this handy questionnaire.
This quiz is exclusively created by Ungex, the mite professionals to help determine if Demodex mites are playing a role in the health of your skin.
Take this online test to estimate your demodex mite population density.
Causes of hair loss
Typically, individuals lose 100 hairs a day and grow approximately the same amount. As long as this balance is preserved, everything goes well. Hair loss occurs when the number of strands lost in a noticeable period is more significant than the number grown or when the hair follicle is destroyed and replaced with scar tissue.
Hair loss is usually connected to one or more of the following:

Heredity (Family History):
Genes have a great influence on hair loss. They can determine the amount or sensitivity to hormones involved in hair loss. The most common type of alopecia in both sexes (androgenic alopecia) is a genetic complication that runs in families. Men who carry the gene often go completely bald, while women only undergo hair thinning.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and thyroid problems can lead to permanent or temporary hair loss.
Medical Conditions and Infections:
Some skin conditions, such as infection with Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton (harmful fungus), can lead to loss of hair in patches. In addition, immune system imbalance causes the body to target the hair follicles, mistaking them with an external threat. This kind of autoimmune defect leads to alopecia areata. Some psychological problems (such as trichotillomania) also give some people strong urges to pull out their own hair.
Medications and Supplements:
Some drugs such as those used in the treatment of cancer, depression, arthritis, heart issues, gout, and high blood pressure can lead to hair loss. On the other hand, radiation therapy to the head can also cause baldness. Fortunately, it is a temporary condition, and hair will come back three to six months after your treatment ends.
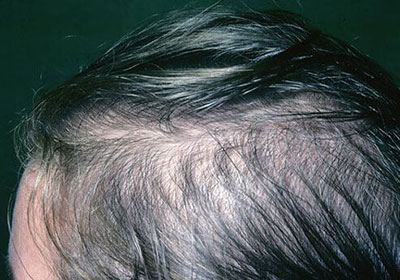
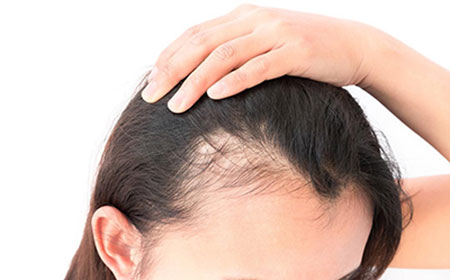
A Very Stressful Event:
Severe physical or emotional stress can cause hair loss after a few months. This condition is called Telogen effluvium and, fortunately, is temporary.
Certain Hairstyles and Treatments:
Excessive hairstyling, keratinization, excessive use of conditioners, hairstyles that pull your hair tight, such as pigtails or cornrows, and the like can lead to hair loss. Although rare, hair may never grow back if scarring occurs.
If you checked and there is no apparent cause for your hair loss, Ungex suggests that you may have Demodex mite issues and may be experiencing Demodex mite hair loss.
What are Demodex mites?
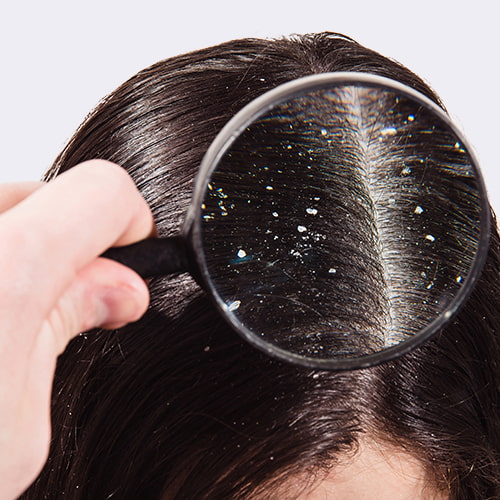
Microscopic organisms have long inhabited human skin. One of them is a tiny parasite called the Demodex mite that resembles insects. Demodex mites are related to spiders and have eight little spider-like legs.
Almost all adults have a population of Demodex on their skin. They acquire these parasites after birth through skin-to-skin contact with their parents as well as infected environmental surfaces. Although we all carry at least a few Demodex mites, they can cause various problems when they become too numerous.
These parasites travel through the skin pores between the surface and the depths. They are so tiny that 25 of them fit into just one follicle.
What Causes Demodex Overgrowth?
Demodex can multiply once the immune system is weak, such as in HIV and AIDS. Or when you are taking immunosuppressive drugs such as corticosteroids. In fact, natural defence controls the organisms that reside on our skin and inside so that they do not increase in a breakout. But if this system fails for some reason, these organisms gain the opportunity to proliferate, leading to various complications.
In addition to immune system issues, individuals with infections and different skin problems are more prone to Demodex parasite infestation. Moreover, direct contact with surfaces that carry a large population of mites allows them to grow and multiply by transferring them to the skin.
The Relationship Between Demodex and Hair Loss
Demodex parasites feed primarily on the sebum made by the skin’s sebaceous glands, which is made under the skin’s pores, near the follicle, right where these parasites live.
Sebum keeps the skin oily and prevents it from drying out. It also provides nutrients for hair strands to grow and remain healthy. Large populations of these mites consume almost all the sebum, leaving nothing to nourish the skin and hair. Starved hairs gradually weaken and eventually fall out. If the skin and hair have already undergone problems, the lack of nutrients limits the strands’ ability to fight the issue, exacerbating the symptoms of the underlying complication.
Apart from the sebum role, Demodex mites secrete inflammatory substances that cause local inflammation, provoke allergy and trigger immune reactions. Inflamed follicles cannot anchor hairs into the skin. The strands gradually loosen and detach from the scalp.
Besides, bacteria, fungi, and viruses live inside these mites, which can trigger hair loss aggravating issues.
Finally, Demodex wiggle around the hair root, physically causing the follicles to stretch and hair to fall out.

Demodex Hair Loss Solution
To discover if Demodex mites play a role in your hair loss, you need to estimate their population on your skin. Ungex Online Demodex Test is a valid questionnaire that helps you find out the rate of Demodex infestation on your skin and hair.
If the results indicate a significant number of parasites, Ungex can help you to reclaim your skin and hair from these damaging parasites.
Ungex skin and hair care products target Demodex and destroy them on the skin. Using these products at night, you can gradually eliminate these parasites within a few months and restore the health of your hair and skin.
Ungex natural and herbal-based products are free of harmful substances such as parabens, SLS, SLES, silicon, and gluten and can kill Demodex in the immediate environments in addition to the skin. This unique feature enables these products to prevent these parasites from spreading to other people in society and within a family.